Push Swap
Efficient Sorting Algorithm Implementation
A sorting algorithm implementation using two stacks with a limited set of operations, focusing on optimization and finding the most efficient way to sort integers.
Key Features
Stack Operations
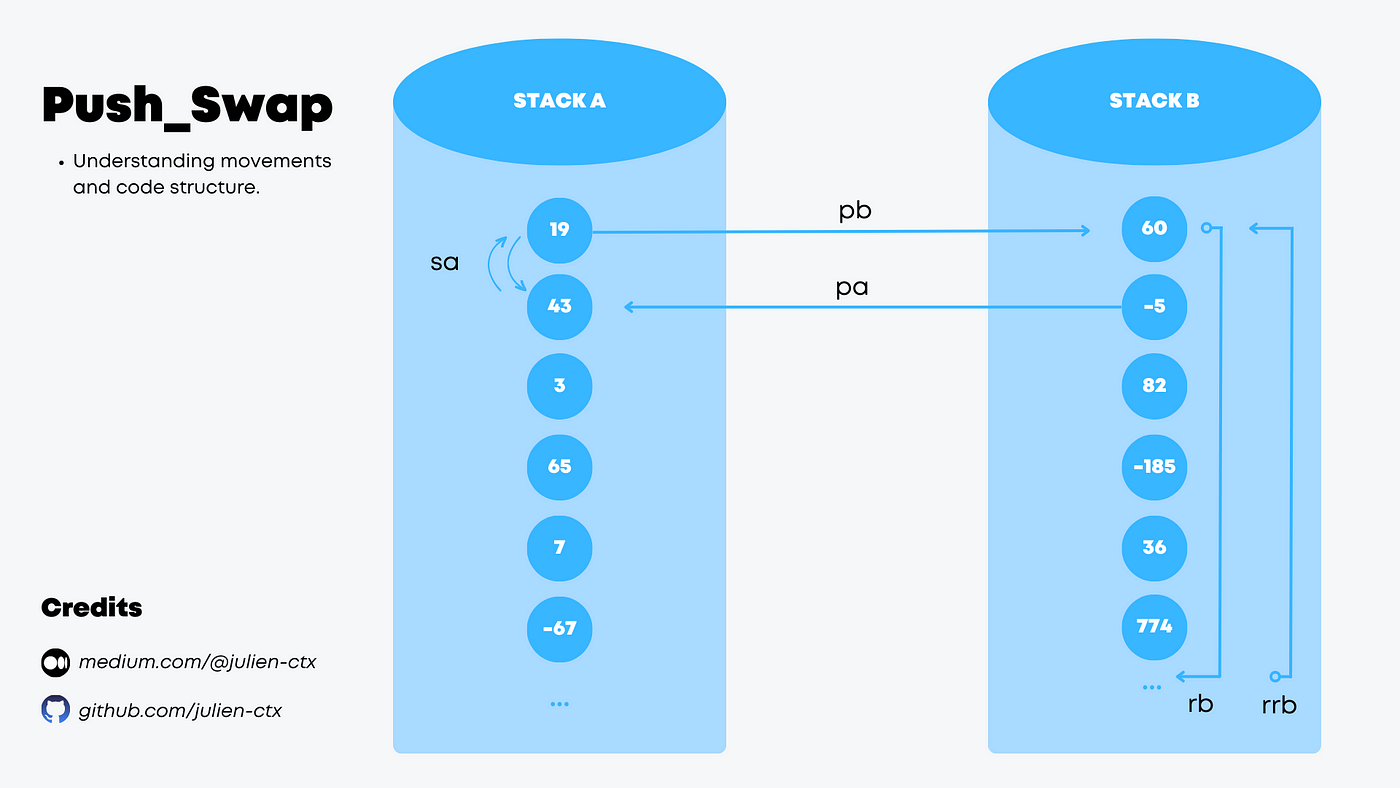
Implemented efficient stack operations including push, pop, swap, rotate, and reverse rotate for both stacks.
Sorting Algorithm
Developed optimized sorting algorithm that minimizes the number of operations required to sort the stack.
Performance Optimization
Achieved sorting with minimal moves, meeting performance benchmarks for different input sizes.
Input Validation
Comprehensive input validation ensuring only valid integers are processed with duplicate detection.
Development Journey
Algorithm Research
Researched various sorting algorithms and analyzed their efficiency for the limited operation set of push_swap.
Stack Operations
Implemented basic stack operations (push, pop, swap, rotate, reverse rotate) with proper error handling.
Sorting Strategy
Developed optimized sorting strategy with chunking for large numbers and efficient rotation patterns.
Challenges & Solutions
Algorithm Optimization
Finding the most efficient combination of operations to minimize total moves while maintaining sorting correctness.
Researched various sorting strategies and implemented a hybrid approach based on input size with radix sort for large datasets.
Large Number Handling
Efficiently sorting large sets of numbers while maintaining optimal performance and meeting move count requirements.
Developed chunking strategy and optimized rotation patterns for large datasets with bit manipulation techniques.
Memory Management
Managing stack memory efficiently while performing numerous operations without memory leaks.
Implemented proper memory allocation and deallocation strategies with comprehensive cleanup functions.
// Stack structure definition
typedef struct s_stack
{
int value;
struct s_stack *next;
} t_stack;
// Main sorting function
void push_swap(t_stack **stack_a, t_stack **stack_b)
{
int size;
size = stack_size(*stack_a);
if (size <= 3)
sort_three(stack_a);
else if (size <= 5)
sort_five(stack_a, stack_b);
else
radix_sort(stack_a, stack_b);
}
// Radix sort implementation for large datasets
void radix_sort(t_stack **stack_a, t_stack **stack_b)
{
int max_bits;
int i;
int j;
int size;
max_bits = get_max_bits(*stack_a);
i = 0;
while (i < max_bits)
{
size = stack_size(*stack_a);
j = 0;
while (j < size)
{
if ((((*stack_a)->index >> i) & 1) == 1)
ra(stack_a);
else
pb(stack_a, stack_b);
j++;
}
while (*stack_b)
pa(stack_a, stack_b);
i++;
}
}
// Stack operation: push from b to a
void pa(t_stack **stack_a, t_stack **stack_b)
{
t_stack *temp;
if (!*stack_b)
return;
temp = *stack_b;
*stack_b = (*stack_b)->next;
temp->next = *stack_a;
*stack_a = temp;
ft_putstr("pa\n");
}